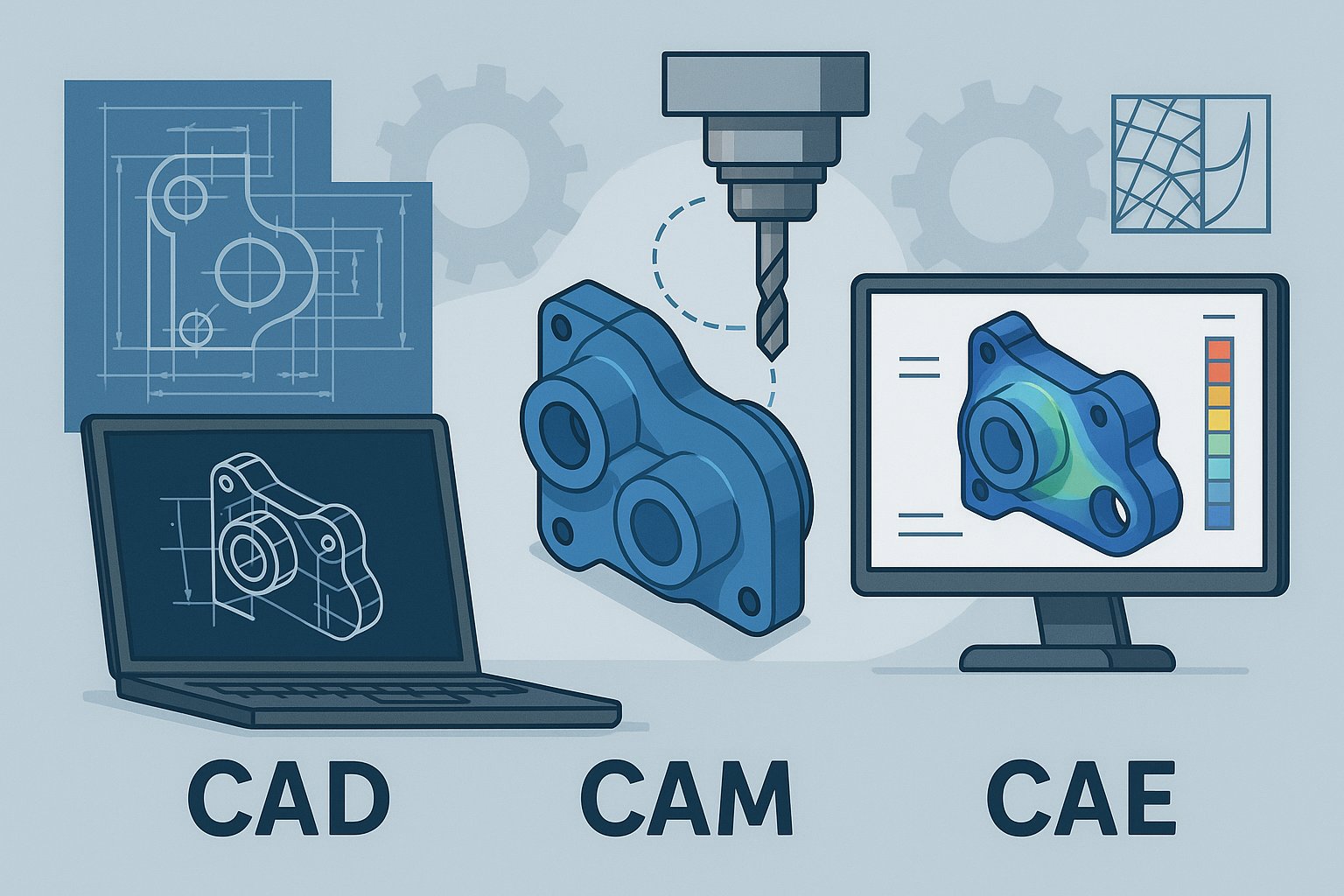

Computer-Aided Design (CAD): CAD software is used to create and modify detailed 2D and 3D models of parts, assemblies, and systems. Designers and engineers use CAD tools to conceptualize ideas, visualize designs, and produce digital prototypes before physical manufacturing begins. CAD software allows for precise manipulation of geometry, incorporation of engineering constraints, and generation of technical drawings and documentation. Examples of CAD software include AutoCAD, SolidWorks, CATIA, and Fusion 360.
Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM): CAM software is used to generate toolpaths and instructions for manufacturing equipment based on CAD models. CAM systems automate the programming of CNC machines, 3D printers (additive manufacturing), and other manufacturing machinery, enabling efficient and accurate production of parts and products. CAM software takes into account factors such as material properties, cutting tools, machining strategies, and machining tolerances to optimize the manufacturing process. Examples of CAM software include Mastercam, HSMWorks, and CAMWorks.
Computer-Aided Engineering (CAE): CAE software is used to simulate, analyze, and optimize engineering designs and processes. CAE tools enable engineers to evaluate the performance, reliability, and safety of designs through virtual testing and analysis. CAE encompasses various disciplines such as finite element analysis (FEA), computational fluid dynamics (CFD), multibody dynamics (MBD), and thermal analysis. Engineers use CAE software to identify design flaws, optimize performance, and reduce the need for physical prototypes and testing. Examples of CAE software include ANSYS, Abaqus, COMSOL Multiphysics, and Simulia.
CAD, CAM, CAE are enabled by these underpinning technolgies:
Together, CAD, CAM, and CAE form an integrated workflow. This integrated approach enables designers and engineers to seamlessly transition from conceptual design to manufacturing, while iteratively refining and optimizing designs based on simulated analyses and manufacturing constraints. This results in more efficient product development processes, reduced time to market, and improved product quality and performance. With CFD, FEA and MBD, these technologies form a comprehensive suite of tools that enable engineers to design, analyze, manufacture, and visualize complex systems with greater efficiency and accuracy.